Automotive relays are electrically operated switches that enable low-current controls, like dashboard switches, to safely power high-current circuits. This includes headlights, fuel pumps and cooling fans.
Why are they important? By using an electromagnetic coil to open and close contacts, relays protect systems from overheating, which ultimately improves a vehicle's reliability and lifespan.
If you're an electrician or trade professional looking to learn more about automotive relays, you're in the right place. This guide covers their functions, types and applications to guarantee a successful installation.
How do automotive relays work?
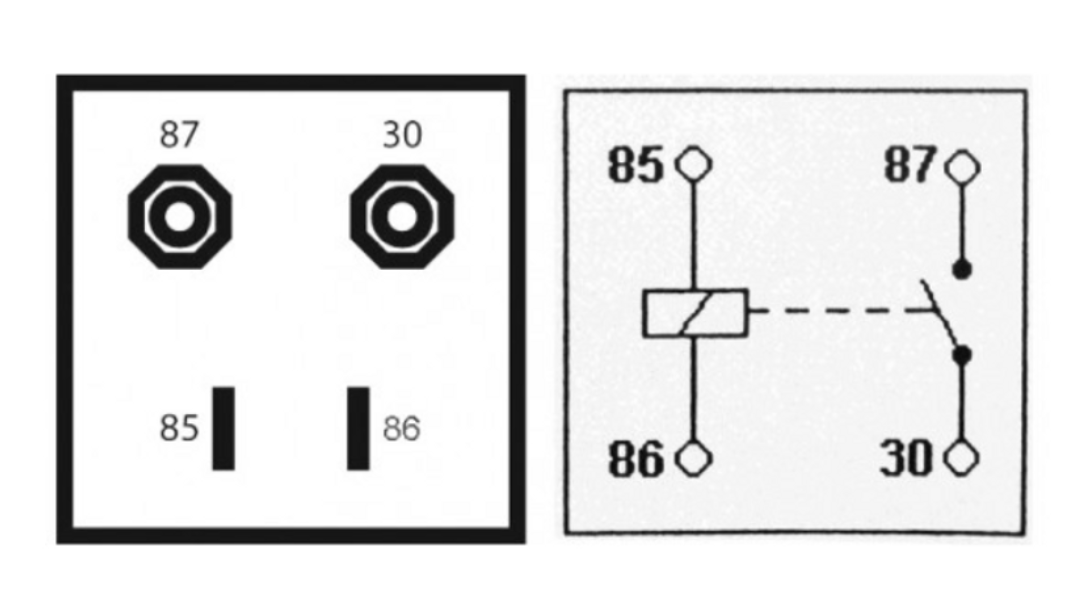
Before we do anything else, let's take a closer look at how automotive relays work. In a nutshell, an internal electromagnetic coil uses low-power electrical signals to operate a switch
When current, usually 12 volts, flows through the coil, it generates a magnetic field that moves a metal armature (a movable part) to open or close a circuit. This allows low-power signals to control higher-power circuits.
Most automotive relays are 12-volt relays, which is the standard voltage for cars. You'll also find 24-volt relays for trucks or heavy equipment, but these are specialised and not typically used in the average repair.
Related reading: What Are the Different Types of Electrical Connectors?
Common types of automotive relays
Not all car relays are the same, so it's important to pick the right one for the job. We’ve listed the main ones below:
- Single pole single throw (SPST) – Functions like an on/off switch for a single circuit with one input (pole) and one output (throw).
- Single pole double throw (SPDT) – Can switch between two circuits with one input and two outputs.
- Time delay relays – Allows users to delay the on/off action. For example, delaying the shutdown of cooling fans after the engine turns off.
- Flasher relays – Similar to the above but specifically designed to make lights blink on and off, like indicators and hazard lights.
- Changeover relays – A type of SPDT that can switch a circuit between two outputs.
Typical applications in vehicles
Relays aren't the most complicated automotive electrical components, but they operate quietly behind the scenes to control several systems in a vehicle, including:
- Exterior and interior lights
- Power seats and windows
- Windshield wipers
- Air conditioning
- Cooling fans
- Fuel pumps
Related reading: Industry Spotlight: Cable Ties, Tape & Consumables in Automotive Sector
Signs of a faulty relay
When an automotive relay is faulty, the symptoms depend on the component it controls. You might notice intermittent or complete failure of systems like the headlights, fuel pump or cooling fans. Sometimes, you'll hear a clicking noise from the relay itself, but the component won't activate – an early sign that the internal switch isn't working properly.
If there's no response at all, noise or otherwise, the relay probably needs replacing completely. In serious cases, a damaged relay can continue to power components even when the engine is off, draining your vehicle's battery.
How to choose the right relay
Not sure which automotive relay is best for the job? Consider the following:
- Pin configuration – Do you need a 4-pin relay or a 5-pin relay? Usually, 4-pins are SPSTs and 5-pins are SPDTs.
- Voltage rating – Make sure the relay is compatible with the vehicle’s voltage system. Typically, it’s 12V for standard cars or 24V for heavier duty applications.
- Housing – Choose between weatherproof or standard relays, depending on the environment.
- OE-style vs universal relays – OE-style relays match the specs of factory parts. Universal relays offer more flexibility but often require custom wiring.

Find reliable automotive relays today
Whether you're searching for a 12V 4-Pin Relay with Resistor or a 24V 5-Pin Micro Relay with Diode, you'll find a quality solution in our product range. From lighting and cooling to fuel systems and wipers, our automotive relays cover a huge range of applications, so you don't have to scour the web to find the right fit.
For more help, speak to a GTSE advisor today.

