Multi-core cables have simplified automotive wiring, making it much easier for mechanics to organise electrical systems. While routing and connecting dozens of single-core cables eventually becomes unmanageable, multi-core cables boast superior space-saving properties for streamlined installations.
Want to learn more? This short guide covers the basics, including cable types, structure and common applications.
What’s inside a multi-core cable?
First things first – what is a multi-core cable? And what makes the design so special?
Typically, multi-core cables share the same basic structure. Inside, you’ll find several individually insulated conductors, or cores, in a single outer sheath. Think of them like a bunch of coloured pencils in a pencil case – each one serves a different purpose, but they're grouped together for convenience.
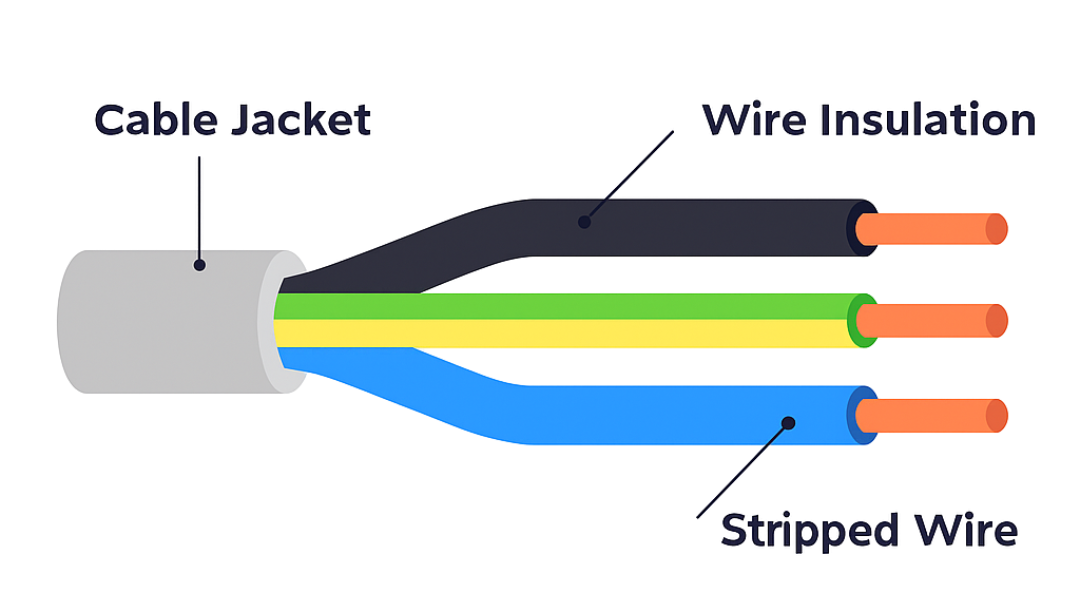
Types by core count
Now we’ve covered structure, let’s explore the most popular core-specific cables used in automotive applications.
Single-core
Single-core cables are exactly what you'd expect – electrical cables containing one insulated conductor. They're commonly used in simple, high-current circuits, such as connecting a battery to the starter motor, grounding points or the main fuse box.
Twin core
As the name suggests, twin-core cables contain two insulated conductors within a single outer sheath. Their simple design makes them ideal for power and ground wiring in basic electrical components, such as headlamps or windshield wipers.
3-core
3-core cables contain three insulated conductors within a single outer sheath – noticing a pattern? This setup supports slightly more complex circuits that require an additional signal wire alongside power and ground.
5-core
5-core cables contain, you guessed it, five insulated conductors within a single outer sheath. As the number of cores increases, so does the complexity of the function. You can use them to power trailer lights, indicators and braking systems.
7-core
7-core cables have seven insulated conductors within a single outer sheath. They support complex automotive applications that require multiple functions to run through a single connection, such as supplying power to caravan lights, interior circuits and charging systems.
13-core
13-core cables contain 13 insulated conductors within a single outer sheath. They support complex automotive and towing systems, such as 13-pin trailer connections, industrial control panels and boating electronics.
Common applications

Multi-core cables are widely used to save space, reduce human error and promote easier vehicle maintenance down the line. Here are five of the most common uses:
- Trailer and vehicle wiring – Connecting towing vehicles to trailers with multiple lighting and power functions.
- Automotive lighting – Powering headlights, taillights and indicators.
- Control boxes in vehicles – Wiring control panels for windows, seats and HVAC systems.
- Central locking systems – Managing signals between door locks and vehicle control units.
- Auxiliary equipment wiring – Supplying power and control signals to additional accessories like roof lights, winches or trailer brakes.
Related reading: Types of Automotive Cables and Applications
Choosing the right cable
So, how do you know which multi-core cable is right for you? Ask yourself the following questions:
- How many cores do you need? The more cores, the more functions. Choose higher core cables for complicated circuits.
- What is the voltage rating? The cable's voltage rating must match the system's voltage rating to prevent insulation breakdown.
- Do you need a flexible cable? Flexible cables are easier to route through tight spaces.
- What colour is the cable? Many industries follow specific colour codes, e.g. red for power and black for ground. This ensures compliance and safety.
Related reading: Specifications for Automotive Cables Defined
Upgrade your installations with the GTSE cable range
At GTSE, we only supply the highest-quality automotive cables and wiring, so you don’t have to worry about your tools letting you down. Our extensive range includes single, twin and multi-core cables – ranging from 3-core to 13-core.
For advice on choosing the right cable, speak to one of our advisors today.

