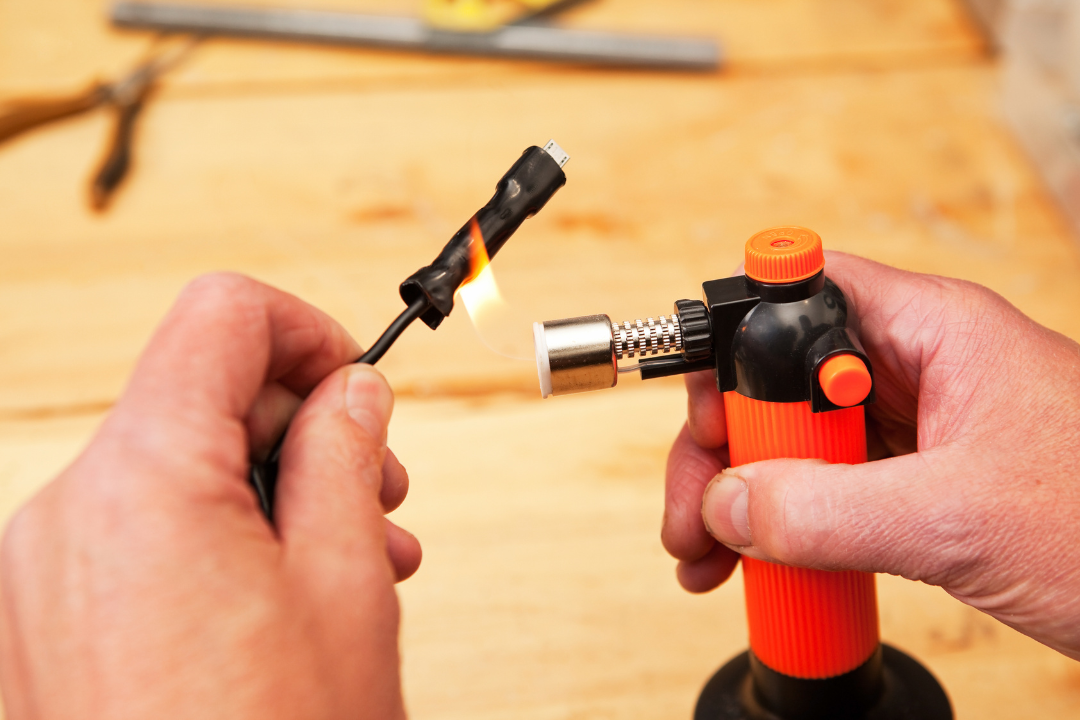
What is Heatshrink tubing?
Heatshrink tubing is a layer of plastic which can be applied to cables and other components for protection, insulation, reinforcement, organizing and identification. These tubes are designed to shrink when heat is applied so that cables have protective coating.

What sort of Materials are Heatshrink made from?
Heatshrink tubing come in a variety of materials for different uses and applications. These include:
- Polyolefin – most common type of material used as it has a high resistance to high temperature and chemical contamination
- Polyvinyl chloride (PVC) – versatile material and relatively cheap to produce
- Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) – high resistance to chemicals and low friction therefore it can be easily taken off after application
- Fluorinated ethylene propylene (FEP) – high resistant to chemicals and shrinks at a lower temperature than materials like PTFE
- Elastomeric – highly flexible and high resistance to abrasion and hazardous chemicals
- Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) – high resistance to flames and chemicals
- Silicone – flexible and excellent to use in various temperature environments. Commonly used to keep fibre optic cables together
- Viton – resistant to high temperature and flexible. Ideal to use to protect wires from oils and other type of hazardous liquids
What are the types of Heatshrink that you can purchase?
There are two types of Heatshrink tubing: single and dual wall.
Single wall tubing – This type of tubing is ideal for use when in electrical insulation or protection against abrasion and strain.
Dual wall tubing – Ideal to use when in need to protect from corrosion or moisture
What accessories can you buy for Heatshrink tubing?
- Connectors – these are used to join cabling together or to connect it to power outlets. These connectors are typically made from polyolefin and when in application they will shrink and melt into place to create a seal.
- Heat shrink wraps – The wrap are a type of heat shrink tubing which is designed to wrap around cables to give an extra layer of protection.
- Heat shrink tape – Typically used to insulate seals. The tape will make the seal more secure
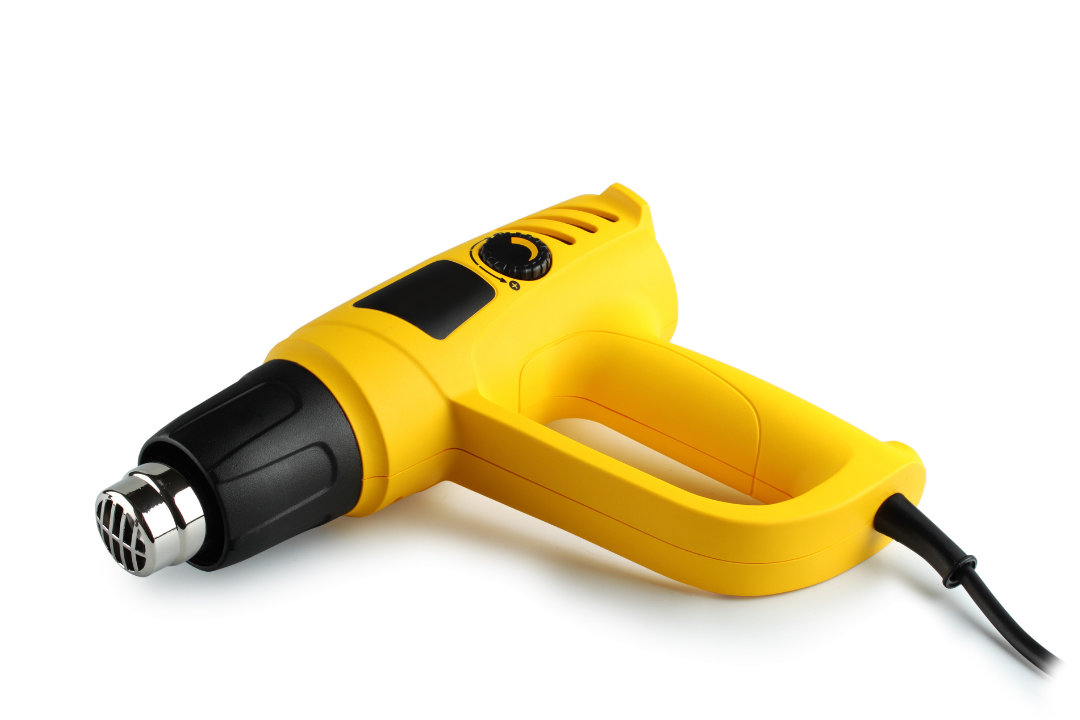
- Heat guns – Heat guns is the go to tool when applying Heatshrink to cables. They work by sending hot air from the nozzle into to the Heatshrink in a safer way than the use of a flame.

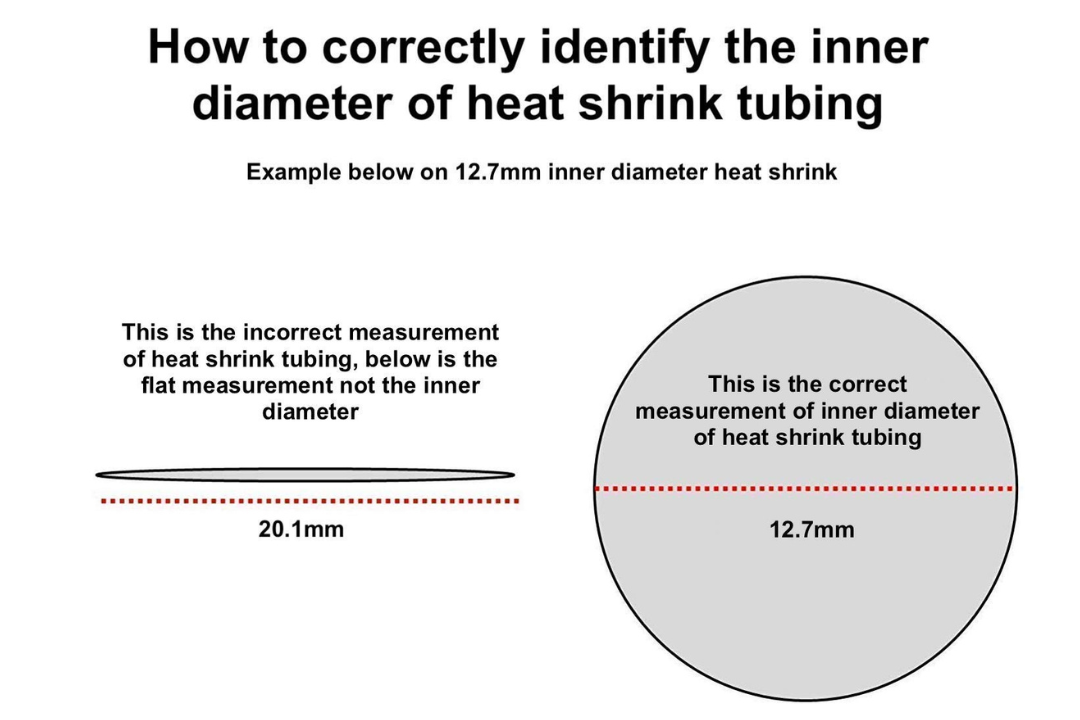
Heatshrink Sizing – Measurement Vocabulary
There are some key vocabulary when dealing with Heatshrink tubing’s measurement .
Inside Diameter or I.D.
The inside diameter of the tubing is measure in inches or millimetres. The tube is measure when it is open and not flattened.
Expanded Inside Diameter or Expanded I.D.
The expanded inside diameter is measured of the inside after the tubing has been expanded. Heatshrink tubing is sold in its expanded inside diameter size.
Lay Flat Width
The lay flat width is the minimum width of the expanded inside diameter heat shrink in its flat form.
Recovered Inside Diameter or Recovered I.D.
When heat is applied to expanded tubing, it will shrink or recover. The recovered inside diameter is the measurement of the inside diameter of the tubing after being allowed to fully shrink or recover back to its original extruded size.
There are four factors that you will need to consider when selecting the correct size Heatshrink tubing
The diameter size of the tubing
Measure the diameter of the underlying materials to be covered by its widest section. Select tubing that is 20% - 30% larger than this measurement.
The shrink ratio
Heatshrink tubing tends to be available in either 2:1 or 3:1 shrink ratios which means that the tubing has been expanded to twice or three times its fully recovered size. The greater the size variation of the underlying materials being covered, the larger the ration required.
2:1 will be the equivalent to a 50% shrink ratio. Example: 50mm to 25mm
3:1 will be the equivalent to 67% shrink ratio. Example: 27mm to 9mm
The wall thickness of the tubing
The wall thickness of the tubing is measure in inches or millimetres and it is the target thickness of the wall after complete recovery.
The length of the tubing
Heat shrink tubing has a small loss of length during the recovery process otherwise known as longitudinal shrinkage. Longitudinal shrinkage can vary from 5% to 10%.
How to apply Heatshrink to wires:
- Make sure the unshrunk piece of tube is fitted to the wire before the connection is made.
- Once you have made the connection, slide the tubing into and position it over the area that requires protection.
- Once in position, heat the tubing so that it shrinks firmly into place. How much it shrinks depends on the type of shrink of tubing that you have used (2:1 or 3:1).
- Most Heatshrink will shrink when heated to 90°C as most materials are made from polyolefin.


